Some aggressive cancers out there have low survival rates, making them very scary. Cancers are especially concerning because we don't know exactly why they happen or how they work. However, the good news about some of the most aggressive, deadly cancers is that many of them are extremely rare and appear to be tied to certain lifestyle choices that we can choose to change. While quitting smoking, for instance, is difficult — the science behind this addiction is clear that nicotine is as addictive as heroin — it is also doable. A lot of cancers, including some of the most aggressive cancers on this list, are connected to tobacco use. We know how hard it is to quit smoking, but it's one of the best things we can do for ourselves.
The deadliest, most aggressive cancers are not necessarily the most common ones. It's also possible to lower the risk of the most common cancers. The same advice about quitting smoking applies — and it's also a good idea to limit alcohol consumption. Many forms of cancer are also connected to excessive alcohol consumption, and other health concerns can arise from drinking too much. While a list of signs and symptoms of cancer may help a person understand the need to visit a doctor, it's also important to avoid trying to diagnose anyone from an article. Simply use information online as a jumping-off point for a conversation with a trusted medical professional, not as a way to be convinced someone we love has cancer. And finally, the really good news: Scientists have made some major advances in cancer treatment in the past 20 years, which gives us all hope.
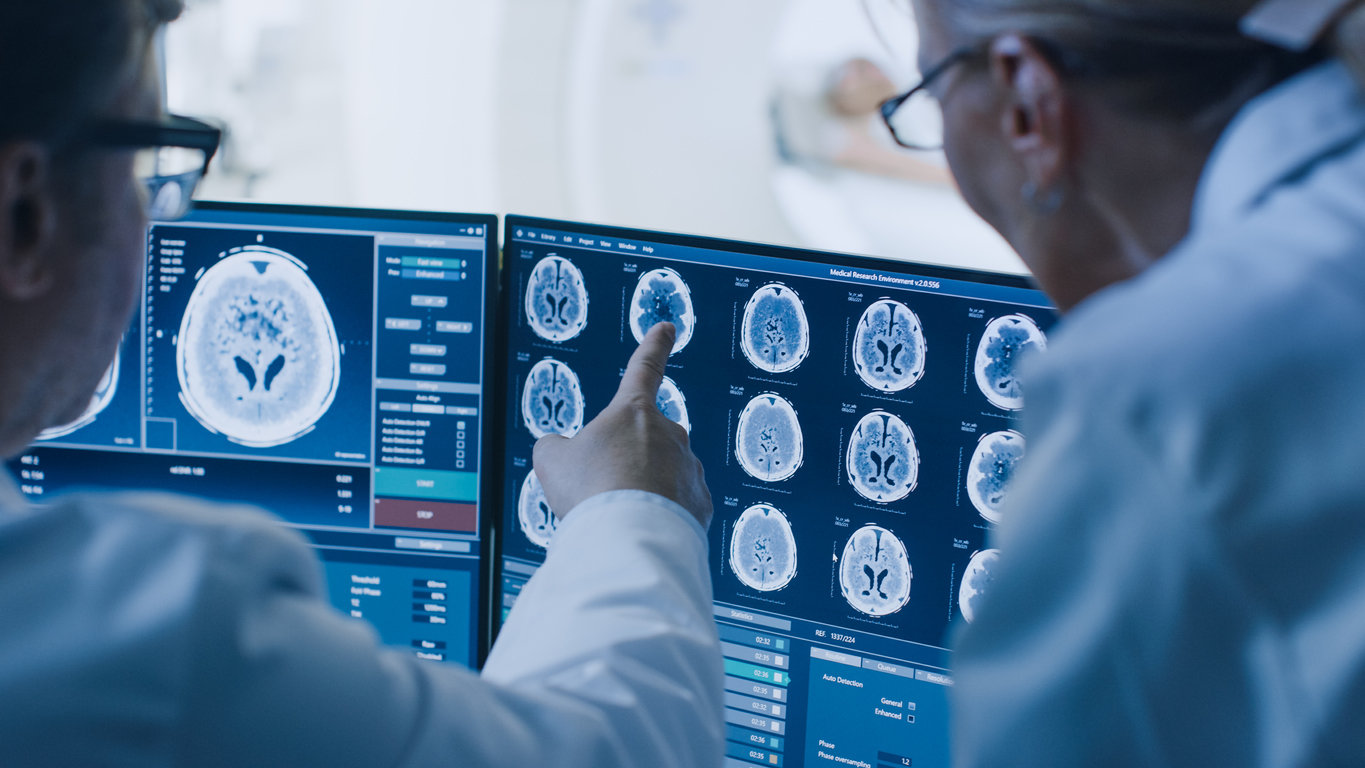
DIPG, or Brain Stem Cancer
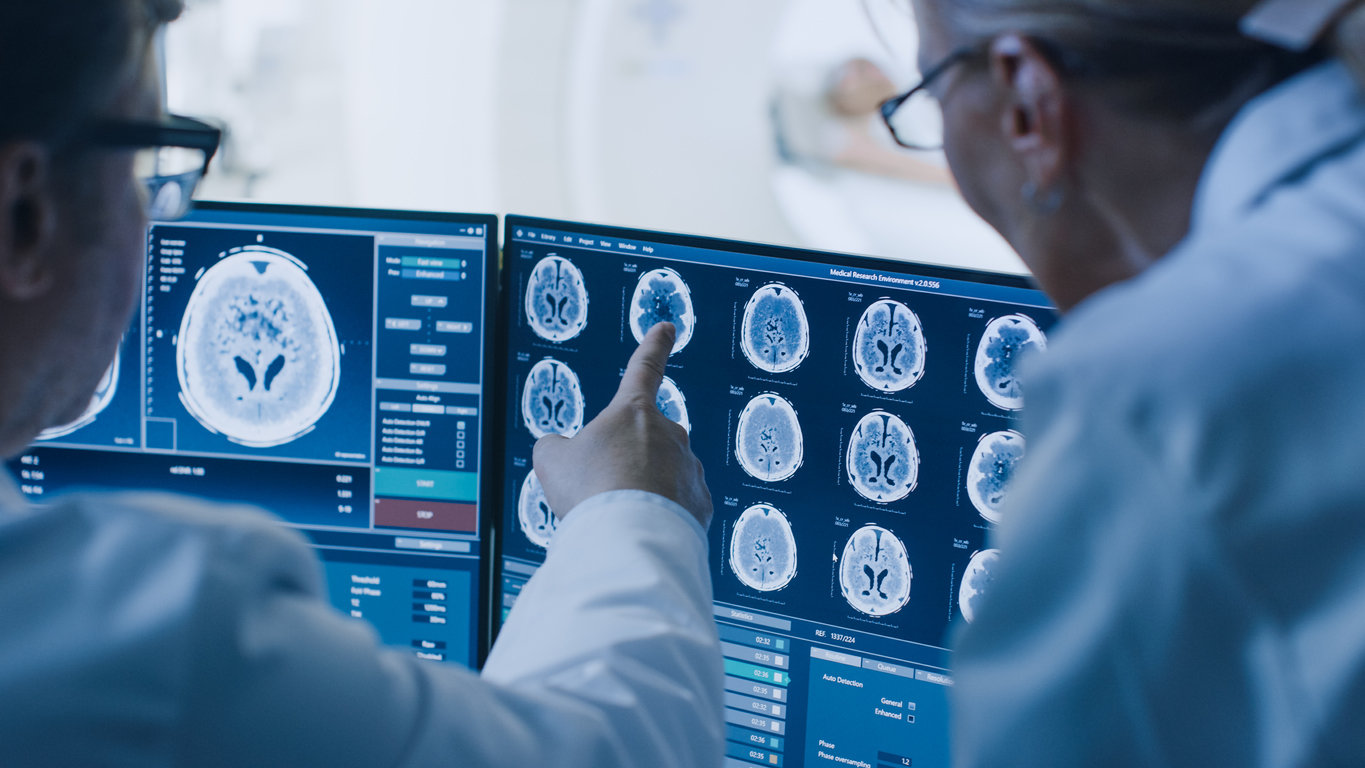
Brain stem cancer is one of the most deadly, having a five-year survival rate of less than 2%. However, while this cancer — which most commonly appears in children — is aggressive, it is also rare, with only 150-300 new patients in the US every year. Scientists do not know what causes it, which makes finding a means of prevention difficult.
Pancreatic Cancer

Pancreatic cancer has several risk factors, but the biggest one is smoking. That is the "most important avoidable risk factor" for this type of cancer, the American Cancer Society reports.
Maintaining a healthy weight is also important for prevention of the disease, which mostly affects people age 55 and older.
Mesothelioma

Mesothelioma is an aggressive, deadly form of cancer that does not currently have a cure. It most frequently affects the tissue around the lungs. The best way to prevent this cancer is by avoiding contact with asbestos, which is directly linked to this disease.
Heart Cancer
Heart cancer is a rare form of cancer that predominately begins as cancer elsewhere in the body, either in the lungs, which are nearby, or spread through the blood. Some types of heart tumors can run in families, so be aware of family health issues.
Bile Duct Cancer

This rare form of cancer occurs in the system that connects the liver, small intestine, and gall bladder. Chances of bile duct cancer are increased for those who have certain liver diseases, so be aware if liver disease is something that is a current concern.
Lung Cancer

The No. 1 cause of lung cancer is smoking. Stop smoking or using any tobacco products to reduce the risk. Also avoid secondhand smoke whenever possible. Smoke from other people’s cigarettes and cigars can negatively affect our health, too.
Gallbladder Cancer

The gallbladder is on the right side of the abdomen, just beneath the liver. This is an uncommon form of cancer, but has a low survival rate. It's more common in older women with a history of gallstones, but it is currently unknown exactly what causes this type of cancer to form.
Esophageal Cancer

High levels of acid in the body could create a higher risk of esophageal cancer. That's why people who have gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) are at an increased risk.
One healthy step to take is to stop smoking. Nicotine in cigarettes loosens the muscles that keep the stomach separate from the esophagus. When that muscle is loosened, the acidic levels in the esophagus rise. Also cut back on or stop drinking alcohol, and exercise to maintain a healthy weight.
Leukemia
Being overweight can increase the risk of leukemia. Eat lots of fruits and vegetables, and stay physically active to maintain a healthy body weight. Also, quit smoking if that's currently a habit. The damage done to the body from smoking can increase the risk of leukemia.
Uterine Cancer

Uterine cancer is cancer of the uterus, and is sometimes called endometrial cancer, named for the layer of cells that line the uterus. While we don't know what causes this form of cancer, there are some risk factors to keep in mind: people who have irregular ovulation patterns due to anything from diabetes, obesity, or polycystic ovarian syndrome; people who began menstruation early; those who have never been pregnant; and anyone who has had hormone therapy for breast cancer.
Stomach Cancer

Stomach cancer, like esophageal cancer, is associated with having GERD, or gastrointestinal reflux disease. It's also associated with smoking and obesity. There is also a connection between a diet high in smoked, salted foods and stomach cancer. Avoiding these foods, not smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight are good steps towards avoiding developing this form of cancer.
Throat Cancer
Throat cancer can refer to several different tumors that occur in the throat or tonsils. It's not clear exactly what causes throat cancer, but risk factors include smoking, chewing tobacco, excessive alcohol consumption, HPV, GERD, and a diet lacking in fruits and vegetables.
Brain Cancer

Brain tumors can develop in a couple of different ways — either by beginning in the brain itself or as a result of cancer spreading from another part of the body.
Some risk factors include exposure to radiation, which can happen if someone is already being treated for another type of cancer, and having a family history (which is rare).
The risk of developing cancer by using radiation-based imaging tests, such as X-rays and CT scans isn't fully known, but to be safe, doctors order these only when absolutely necessary.
Ovarian Cancer
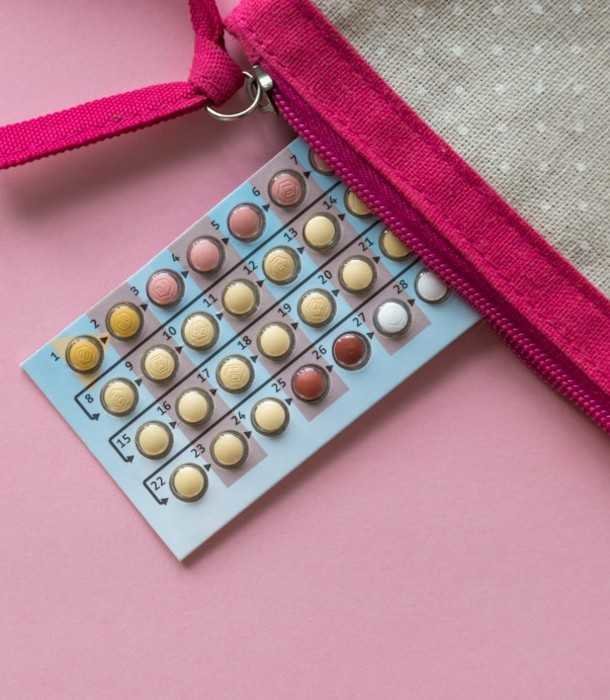

While there is no known way to prevent ovarian cancer, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend staying on birth control pills for five years or longer. The hormonal regulation of the body helps to lower the risk of ovarian cancer. Removing ovaries or having a tubal ligation can also help reduce the risk. There is also a lower risk for those who have given birth or have breastfed for a year or longer.
Tracheal Cancer

Tracheal cancer, which occurs in in the windpipe, is rare. But there is an almost direct correlation here: smoking. For any smokers looking to avoid cancer of this form, quitting smoking is a great first step.



